the price of BTC

What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a digital currency system that operates independently of banks or central authorities. All transactions are recorded on a blockchain maintained by a decentralized global network of nodes. Key features include a fixed maximum supply of 21 million coins and the use of Proof-of-Work (PoW) with the SHA-256 hashing algorithm, allowing miners to compete in securing the network by validating transactions.
Instead of traditional account balances, Bitcoin uses the UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) model, where your balance consists of all unspent outputs you control. This model enhances parallel processing and network security. With its capped supply, censorship resistance, and global accessibility, Bitcoin is often viewed as a “store of value” or “digital gold,” while also supporting peer-to-peer transfers and payments.
What Is the Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of Bitcoin (BTC)?
As of 2025-12-23 16:22 (UTC), Bitcoin trades at approximately $87,861.78 per coin, with a circulating supply of 19,966,056 BTC, total supply matching at 19,966,056 BTC, and a maximum supply capped at 21,000,000 BTC. The circulating market capitalization is around $1,754,253,213,433.60, with a fully diluted market cap near $1,845,097,373,367.36. Bitcoin’s dominance in the overall crypto market stands at 59.2416%. Price changes include +0.6335% over the past hour, -2.3747% in 24 hours, -0.1486% over 7 days, and +0.9633% in the past 30 days. The 24-hour trading volume is about $42,752,258,960.04 across 12,503 trading pairs.
Market capitalization (circulating) is calculated as “current price × circulating supply.” Fully diluted market cap uses “current price × max supply.” Dominance reflects Bitcoin’s proportion within the total crypto market cap. These metrics help users evaluate scale, volatility, and relative market position.
Who Created Bitcoin (BTC) and When?
Bitcoin was introduced by the pseudonymous “Satoshi Nakamoto,” who published the whitepaper “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” in 2008. The genesis block was mined in 2009, marking the network’s launch. As more people joined mining and usage grew, Bitcoin began trading publicly around 2010 and gained wider recognition.
After contributing to early code development and community growth, Satoshi Nakamoto gradually withdrew from active involvement. Since then, Bitcoin’s ecosystem has been maintained by a global community of developers and node operators. Bitcoin’s issuance rate is controlled through scheduled “halving” events that reduce block rewards over time, slowing inflation.
How Does Bitcoin (BTC) Work?
Bitcoin’s blockchain records every transaction ever made. Miners use the PoW mechanism to solve complex SHA-256 hash puzzles—whoever finds a valid solution first packages the next block and receives a block reward plus transaction fees. A new block is mined roughly every 10 minutes; the mining difficulty is periodically adjusted according to network hash rate to maintain this schedule.
Transactions are authorized using private keys and broadcast across the network. The private key is a cryptographic code that allows you to spend funds—its security is crucial—while the public key and address receive funds. The UTXO model means each output can be spent separately, increasing scalability and security. Over time, as block rewards halve periodically, transaction fees are expected to make up a larger share of miner incentives for network sustainability.
What Can You Do With Bitcoin (BTC)?
- Store of Value: Many hold Bitcoin long-term as a hedge against fiat currency inflation and geopolitical uncertainty.
- Peer-to-Peer Payments: Bitcoin enables global transfers without banks or intermediaries.
- Merchant Settlement: Some businesses accept BTC for goods or services in direct online payments.
- Scalable Micropayments: To enhance everyday payment efficiency, Bitcoin supports scaling solutions like the Lightning Network—a state channel technology enabling faster and cheaper off-chain transactions with final settlement on-chain for security.
What Wallets and Scaling Solutions Exist in the Bitcoin (BTC) Ecosystem?
-
Wallets:
- Hot Wallets: Connected to the internet for frequent transactions.
- Cold Wallets: Offline storage for long-term holding and enhanced security against online attacks.
- Hardware Wallets: A type of cold wallet that stores private keys offline in dedicated devices.
-
Scaling Solutions:
- Lightning Network: Enables high-frequency micropayments with low fees.
- Multi-Signature (Multisig): Distributes transaction authorization across multiple keys for higher asset security.
- Light Clients (SPV): Allow users to verify transaction headers without downloading the entire blockchain—balancing convenience with basic security.
Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for Bitcoin (BTC)
- Price Volatility: Bitcoin’s price is highly sensitive to market sentiment, macroeconomic trends, and policy changes—sharp short-term fluctuations are common.
- Custody & Private Key Risks: Loss or theft of your private key means permanent loss of assets; securely store seed phrases and avoid phishing or malware threats.
- Network & Fee Risks: Network congestion can increase transaction fees and confirmation times, impacting payment reliability.
- Platform & Compliance Risks: When depositing or trading on exchanges, understand their policies and risk controls; use two-factor authentication for added security. Regulatory requirements for crypto assets vary across jurisdictions—always comply with local laws before transacting.
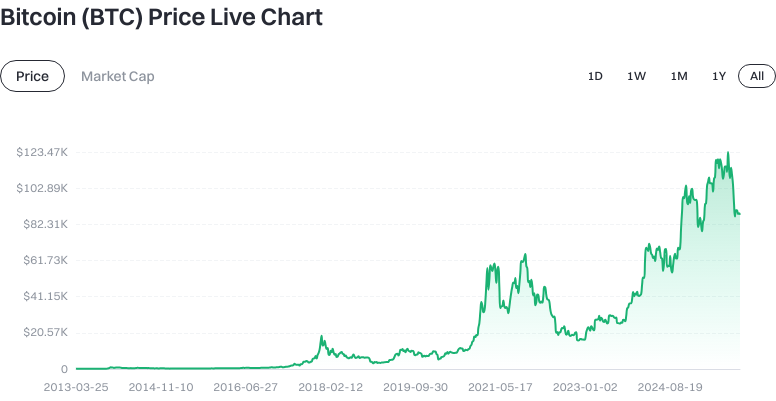
Click to view latest BTC price chart
How to Buy and Securely Store Bitcoin (BTC) on Gate
Step 1: Register and Complete Identity Verification Visit gate.com to create an account and follow on-screen instructions to verify your identity—this increases limits and account security.
Step 2: Enable Account Security Activate two-factor authentication (2FA), withdrawal whitelist, and anti-phishing codes to minimize risk of account compromise.
Step 3: Deposit or Fund Your Account You can buy USDT via fiat channels before converting to BTC or transfer USDT/BTC from another wallet to your Gate account—always double-check the correct network and tag information.
Step 4: Select Trading Pair and Place Order Search for “BTC/USDT” in spot markets; choose between market orders (execute at current price) or limit orders (set your own price). Always confirm amounts and fees before submitting.
Step 5: Withdraw to Your Own Wallet For long-term holding, transfer BTC to a self-custody wallet. Use the “Withdraw” feature—select BTC chain as the network and paste your receiving address. Start with a small test withdrawal before moving larger amounts.
Step 6: Store and Back Up Securely Use a hardware wallet or properly stored cold wallet; write down your seed phrase offline and create encrypted backups; regularly check devices and update firmware—never expose private keys online.
How Does Bitcoin (BTC) Differ from Ethereum?
- Positioning & Use Cases: Bitcoin focuses on being a decentralized store of value and payment system; Ethereum is a programmable smart contract platform supporting DeFi, NFTs, and various applications.
- Consensus & Energy Consumption: Bitcoin uses PoW with SHA-256 for security; Ethereum now utilizes Proof-of-Stake (PoS), where validators secure the network through staking—significantly reducing energy consumption.
- Supply & Issuance: Bitcoin has a fixed maximum supply of 21 million coins with new issuance decreasing via halvings; Ethereum has no hard cap—net supply is affected by both issuance and mechanisms like EIP-1559 burning.
- Performance & Fees: Bitcoin blocks are mined every ~10 minutes; fees rise during congestion. Ethereum’s mainnet processes blocks faster with smart contract capabilities but also experiences high gas fees at peak times; Layer 2 solutions are used for scaling.
Summary of Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin stands as the most established decentralized digital currency globally, featuring fixed supply, PoW-based security, and broad consensus that underpin its role as a “store of value.” It leads in market capitalization and trading activity but remains subject to cyclical price swings and fluctuating fees. If you prioritize long-term scarcity and global accessibility, you can acquire BTC on Gate using secure procedures—and safeguard it via hardware wallets and strict private key management. Whether you hold for investment or use it for payments, always consider volatility, platform reliability, and regulatory compliance. Start with small transactions using stepwise onboarding to develop robust crypto asset management habits.
FAQ
How Should Beginners Manage Bitcoin’s Price Volatility?
BTC price volatility is driven by supply-demand dynamics, macro policies, and investor sentiment—it’s a normal market phenomenon. Beginners may consider dollar-cost averaging (DCA)—buying small amounts at regular intervals rather than making lump-sum purchases. Set stop-loss/take-profit thresholds to avoid emotional decisions and stay rational.
What Are the Main Factors Influencing BTC’s Price?
Four major factors impact BTC price:
- Global macroeconomic conditions (central bank policies, inflation data)
- On-chain data (large holder movements, transaction activity)
- Regulatory changes
- Shifts in market sentiment
Understanding these factors helps interpret price trends—but remember, no one can predict short-term moves with certainty.
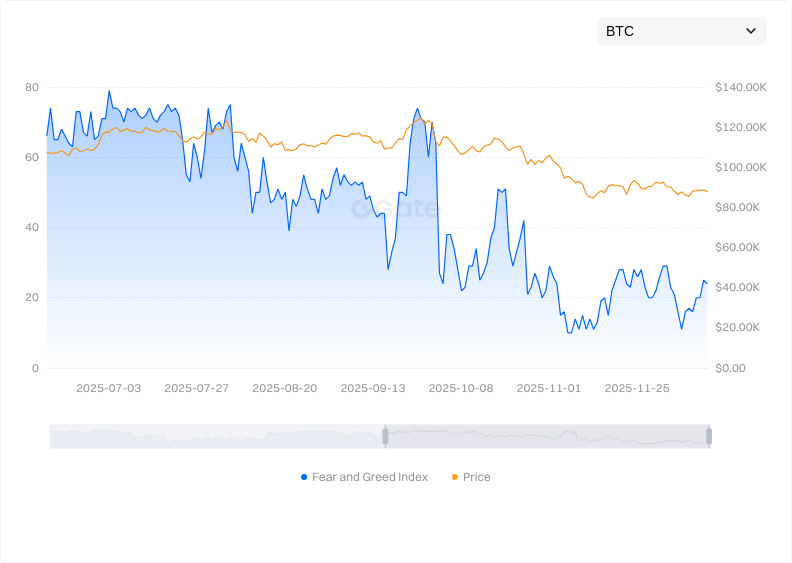
Click to view BTC Fear & Greed Index
What Should I Watch When Checking BTC Price on Gate?
When viewing BTC prices on Gate, distinguish between spot price, futures price, and margin trading price—as market conditions can cause discrepancies. Compare multiple trading pairs (like BTC/USDT or BTC/USDC) for accurate reference to avoid decisions based on outlier quotes.
What Was BTC’s All-Time High Price—and Why Did It Reach That Level?
BTC reached an all-time high near $69,000 in November 2021. The surge was driven by several factors: significant institutional inflows, expectations around spot Bitcoin ETFs, abundant global liquidity, and widespread FOMO sentiment. All-time highs often signal overheated markets—investors should remain cautious.
Why Do BTC Price Moves Often Affect Other Cryptocurrencies?
As the market leader, BTC’s price direction typically drives the broader crypto market—a phenomenon known as “Bitcoin dominance effect.” When BTC rises, investor risk appetite usually increases toward other assets; when it falls, risk appetite declines—making BTC trend tracking vital for portfolio management.
Bitcoin (BTC) Key Term Glossary
- Mining: The process of competing via computational power to validate transactions and earn new coins as rewards.
- Proof-of-Work (PoW): The consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin; requires expending computational resources to secure the network.
- Block Reward: The bitcoins earned by miners who successfully add new blocks to the blockchain.
- Halving: An event roughly every four years where block rewards are cut in half to control supply issuance.
- UTXO: Unspent Transaction Output—the basic accounting unit in Bitcoin’s ledger model.
- Hash Rate: The number of hash computations performed per second by the network—a key indicator of security.
Further Reading on Bitcoin (BTC)
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Developer Docs:
-
Authoritative Media / Research:
Related Articles
 0
0Staking Explained | Gate Web Tutorial Series
 0
0Gate Broker Program Explained
 0
0