歴史上最大の暗号資産ハッキングトップ10
この記事では、歴史上で最も驚愕の暗号資産ハッキングトップ10について掘り下げます。悪名高いハッカーグループ、一般的な攻撃手法、暗号資産の世界で使用される洗浄された巧妙なマネーロンダリング技術を探求します。さらに、従来のハッキングと暗号資産ハッキングを比較し、投資家が潜在的なリスクを回避するのに役立つ貴重なセキュリティのヒントを提供します。概要
暗号資産の台頭は富と革新をもたらしましたが、重大なセキュリティリスクも導入しました。ハッキング攻撃は暗号資産業界で依然として悩みの種であり、過去10年間で数十億ドルが盗まれています。以下は、業界に長い影響を与えた歴史上で最も影響力のある暗号資産ハッキングのリストです。
例えば、2024年には、ハッキングによる損失が22億ドルに上り、前年比21.07%増加しました。特に、2024年1月から7月にかけてハッキング活動が急増し、北朝鮮のサイバー犯罪者が13.4億ドル以上を盗み、総損失の61%を占めています。
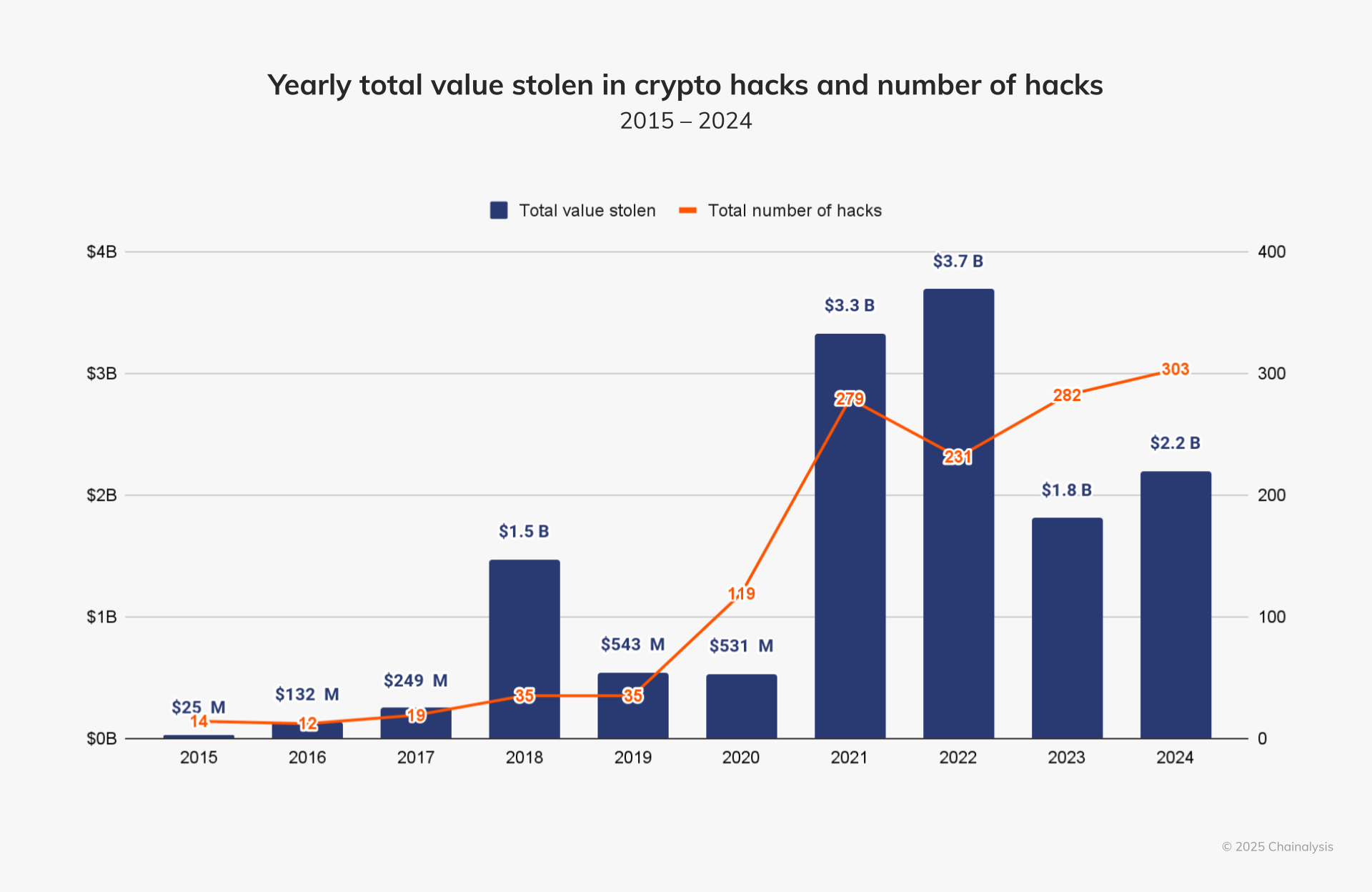
ソース:https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/crypto-hacking-stolen-funds-2025/
トップ10の暗号資産ハック
世界の仮想通貨業界では、複数の大規模なハッキング事件が発生しており、2025年2月に発生した最大の被害は、14億6,000万ドルが盗まれたBybitのハッキングです。ハッカーは、高度なフィッシング攻撃とスマートコントラクトの脆弱性を利用して、コールドウォレットからETHを抽出しました。2番目に大きなハッキングは、2022年3月に発生したRonin Network攻撃で、ハッカーがAxie Infinityのサイドチェーンバリデータノードを制御し、ETHとUSDCで6億2500万ドルを盗みました。
その他の主要な攻撃には、次のものが含まれます:
- Poly Network cross-chain bridge exploit (2021) – $611 million stolen
- Binance BNBブリッジハック(2022年)- 569百万ドル盗難
- Coincheck exchange hack (2018) – $534 million stolen
- Mt. Gox取引所の崩壊(2014年)- 473百万ドル盗まれました
さらに、FTX、Wormhole、DMM Bitcoin、およびKuCoinなどのプラットフォームも重大なハッキング被害を被っています。一部の損失は保険および補償措置を通じて回収されましたが、これらの出来事は暗号資産業界内の深刻なセキュリティリスクを示しています。


ソース: https://cointelegraph.com/news/kucoin CEOは、2020年の285百万ドルのハッキングからの損失の16%を保険がカバーしたと述べた
影響と将来の展望
業界全体のトレンドと主要なセキュリティ問題
(1) クロスチェーンブリッジは高リスクの標的です
クロスチェーンブリッジは、その複雑さと資産移転の高いボリュームのため、ハッカーの主要な標的となっています。複数のチェーン間でのオペレーションを調整する必要性は、脆弱性の可能性を増加させます。
主要なインシデント:
- Poly Network (2021): $613 million stolen, exposing the risks in cross-chain smart contracts.
- Binance BNBブリッジ(2022年):バリデーションの脆弱性を悪用され、5億7000万ドルが盗まれました。
- Wormhole (2022): 3億2600万ドルが盗まれました。スマートコントラクトの検証メカニズムに欠陥があるためです。
業界への影響:
- 強化されたクロスチェーンブリッジセキュリティ設計、マルチシグネチャーおよびMulti-Party Computation(MPC)技術を組み込んでいます。
- トラディショナルクロスチェーンブリッジの代替として、ロールアップやネイティブインターオペラビリティソリューション(例:LayerZero)にシフトする。

ソース: https://www.halborn.com/blog/post/explained-the-wormhole-hack-february-2022
(2) Cold/Hotウォレット管理の脆弱性
冷ウォレットであっても完全に安全とは限りません。ハッカーは、防御をバイパスするためにフィッシング攻撃、ソーシャルエンジニアリング、または内部アクセスの脆弱性を利用します。常にインターネットに接続されているホットウォレットは、高リスクな標的のままです。
主要なインシデント:
- Bybit (2025) (予定): ウォレットの管理ミスによる取引所ハッキング、潜在的な損失は不明。
- Coincheck (2018): NEMが盗まれ、ホットウォレットにはマルチシグネチャ保護が欠けていました。
- KuCoin (2020): $280 million stolen, as hackers gained access to private keys and took control of hot wallets.
業界への影響:
- 取引所は、冷たいウォレットの使用を増やし、マルチシグネチャ認証とハードウェアセキュリティモジュール(HSM)を強化しています。
- 「Proof of Reserves」透明性メカニズムの採用により、中央集権型の保管リスクに対する懸念が軽減されています。

ソース: https://www.ic3.gov/PSA/2025/PSA250226
(3) サイドチェーンと新興技術の弱点
2022年のRonin Network攻撃は、サイドチェーンや新しいブロックチェーン技術の脆弱性を露呈しました、特にバリデーターのセキュリティに関して。多くのブロックチェーンゲームやサイドチェーンは、分散度が低い状態で運営されており、ハッカーにとって侵害しやすい状況にあります。
重大インシデント:
- Ronin Network (2022): ハッカーたちは9つのバリデータノードのうち5つを制御し、6億2000万ドルを盗みました。
業界への影響:
- プロジェクトは、バリデータの分散化を強化し、ノードの数を増やし、コンセンサスのセキュリティを向上させています。
- GameFiおよびNFTに焦点を当てたサイドチェーンは、ArbitrumやOptimismなどのレイヤー2ソリューションに移行し、セキュリティを向上させています。

ソース: https://www.technologyreview.com/2022/04/15/1050259/a-620-million-hack-just-another-day-in-crypto/
(4) 中央集権取引所(CEXs)におけるシステミックリスク
中央集権型取引所(CEXs)は設計上脆弱であり、その中央集権型の構造により、管理の失敗、内部者による詐欺、外部からのハッキングの脅威にさらされています。
主要インシデント:
- Mt. Gox(2014年):850,000 BTC盗難(今日価値で約$4.7B相当)、市場を揺るがす。
- FTX(2022):詐欺的な管理により、顧客資金80億ドルが不正使用されました。
- DMM Bitcoin(2024):取引所のセキュリティプロトコルの脆弱性が露呈される大規模ハッキング事件。
業界への影響:
- CEXsは、準備金の証明と資産分離方針の提出を求められる厳しい規制に直面しています。
- より多くのユーザーが非中央集権型取引所(DEXs)に移行し、自己保管ウォレットの需要が増加しています。
これらの出来事は、業界全体にセキュリティ問題へのより大きな重点を置くよう促してきました。技術的な観点からは、業界はウォレット管理、スマートコントラクトの監査、およびクロスチェーンブリッジのセキュリティ設計への投資を増やしてきました。経営の観点からは、中央集権的なプラットフォームは内部アクセス制御と従業員の教育を強化することを余儀なくされています。しかし、セキュリティの課題は、特に新技術の急速な進化の中で、業界の発展の根本的なボトルネックとなっています。
規制トレンドとコンプライアンスの加速
ハイプロファイルなハッキング事件は、主要な金融損失や広範な影響(例:Mt. Gox、FTX)に続いて、規制当局の監視を直接的に高めました。その結果、世界的な規制トレンドは以下のように進化しています:
規制上のギャップから構造化された監視へ
2014年のMt. Goxハックが発生した際、暗号資産業界にはほとんど規制がなく、投資家が損失を回収するのが困難でした。2020年代には、主要な管轄区域である日本(Coincheckハック後)、EU(MiCAフレームワークを通じて)、米国(FTX崩壊後のSEC取り締まり)が厳格な規制の実施を開始しました。これらの規制には、暗号資産取引所に対するKYC/AMLコンプライアンス、資産の分離、定期的な監査が必要とされています。

ソース: https://www.fsa.go.jp/en/news/2022/20221207/01.pdf
クロスチェーンブリッジ&DeFiの規制
Poly NetworkやWormholeなどのハッキング事件は、分散型金融(DeFi)における規制の盲点を露呈しました。将来、規制当局はオンチェーンのトラッキング技術を通じてDeFiを監視しようとするか、プロトコル開発者が自らの身元を開示することを要求するかもしれません。その際、革新が窒息しないようにも配慮する必要があります。
より厳格なコールド/ホットウォレット管理基準
Bybit(2025年)とKuCoin(2020年)へのハッキング事件により、規制当局は取引所ウォレットのセキュリティに焦点を当てるようになった。将来の規制には、取引所に対する強制的な冷蔵庫保管要件や定期的な公開の準備金の証明開示が含まれる可能性がある。
影響:
より強力な規制は、特に小規模取引所にとっては短期的なコンプライアンスコストを増加させるかもしれません。しかし、これらの措置は業界を標準化し、長期的にはシステムリスクを軽減するのに役立ちます。日本のコインチェック後の規制は広範囲にわたる冷蔵庫の採用につながりました。一方、FTXの崩壊は取引の透明性への世界的な要求を加速させました。
産業信頼の再構築への道
暗号資産のハッキングは、特にMt. GoxやFTXのような事件で大規模なユーザー損失が発生した後、投資家の信頼を大きく損なっています。信頼を回復するには、技術と制度上の保護策の両方を改善する必要があります:
技術的透明性の向上
KuCoin(2020年)やWormhole(2022年)などの事件は、ブロックチェーンの透明性が危機管理に役立つことを示しており、一部の盗まれた資金がオンチェーントラッキングやプロトコルの修正を通じて回収されました。将来的には、準備金の証明(PoR)が業界標準となり、中央集権的なプラットフォームが資産の準備金を定期的に開示することが求められるかもしれません。

ソース: gate.io
補償と保険メカニズム
Coincheck(2018年)およびDMM Bitcoin(2024年)は、企業資金や保険を通じてユーザーに補償を行い、信頼問題を軽減しました。これは、将来的に業界全体の保険基金や強制的な補償メカニズムが登場する可能性を示唆しています。伝統的な金融と同様に、預金保険モデルが暗号資産市場に徐々に導入される可能性があります。

Source: relminsurance.com
成長する分散化トレンド
ロニンネットワーク攻撃(2022年)の後、業界は分散型検証メカニズムの必要性を再評価し始めました。分散型取引所(DEX)や自己保管ウォレットの台頭により、ユーザーは中央集権型プラットフォームへの依存を減らし、リスクを軽減することができます。
信頼の再構築は長期的なプロセスです。短期間では、投資家は主要取引所または完全に分散化されたソリューションに傾きます。長期的には、業界が技術革新と自己規制を通じてハッキング事件の頻度を減らすことができれば、信頼危機は徐々に緩和されるかもしれません。
悪名高い暗号資産ハッキンググループ
暗号資産空間でのハッキング攻撃は、しばしば技術的な脆弱性、ソーシャルエンジニアリング、その他の手法を悪用する熟練したサイバー犯罪組織によって行われます。資金を盗むために。
以下は、公開された報告書や歴史的な事件に基づいて、暗号資産業界で悪名高いいくつかのハッキンググループの概要です。これらのグループの正確な身元や所属は確認するのが難しいことが多く、一部の帰属は推測に基づく可能性がありますことに注意することが重要です。

異なるハッカーグループは、暗号資産業界に異なる影響を与えます。Lazarus Groupのように、直接の暗号資産の盗難に焦点を当てるものもありますが、DarkSideやREvilのような他のグループは、主に暗号通貨の支払いを要求するランサムウェア攻撃を行っています。彼らの正体や所属は、一般報道、法執行機関の発表、またはサイバーセキュリティの分析に基づいており、そのため、一部の主張は議論の余地があります。
暗号資産ハッキンググループが深い秘匿性の中で活動していることを理解することは重要です。これは、起因の特定が困難であり、時に政治的に影響を受けることもあります。さらに、技術の進歩とともに、新しいハッカーグループが現れる可能性が高いため、暗号資産のセキュリティは常に闘い続けることになるでしょう。
サイバー攻撃と防御対策
ハッカーは、フィッシング、マルウェア、ランサムウェア、サービス拒否(DoS)、SQLインジェクション、スマートコントラクトの脆弱性、51%攻撃を含むさまざまな方法を通じて攻撃を開始することができます。これらのそれぞれが、財務損失やシステムの障害のリスクをもたらします。
ただし、2要素認証(2FA)、ウイルス対策ソフトウェア、ウォレットのバックアップ、暗号化されたネットワーク、定期的なセキュリティ監査などの防御策を講じることで、これらのリスクを軽減することができます。


Source: cointelegraph.com
資金洗浄の方法と予防策
マネーロンダリングの手法には、コインミキサー、クロスチェーンブリッジ、非中央集権取引所(DEX)、店頭取引(OTC)、一括取引、取引分割が含まれます。
予防対策には、複数のウォレットアドレスを使用し、定期的に取引履歴を確認し、クロスチェーンブリッジのセキュリティをチェックし、信頼できるDEXプラットフォームを選択し、OTC取引の取引相手を検証し、異常な大口取引を監視し、取引所間の資金流れ規制を強化することが含まれます。これらの手順は、マネーロンダリング活動を特定して防止するのに役立ちます。

暗号資産ハッカーと従来のハッカーの比較
暗号資産ハッキング攻撃と従来のサイバー攻撃は、技術、ターゲット、影響、防御策の観点で大きく異なります。暗号資産ハッカーは、ブロックチェーンや仮想通貨の脆弱性を悪用することに焦点を当てていますが、従来のハッカーは主にITインフラストラクチャやネットワークセキュリティの弱点を標的としています。
暗号資産が一般的になるにつれ、セキュリティの強化、規制の強化、ユーザーの意識向上が重要になり、この種の攻撃を減らす上で重要になります。


ソース: https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/WannaCry_ransomware_attack
個人投資家向けの投資のヒント
リスクを軽減するために投資を分散させる
ハッカーの攻撃は、単一のプラットフォームやプロジェクトのセキュリティ侵害が重大な損失につながることを示しています。複数のプラットフォームやプロジェクトに資金を分散させることで、投資家のポートフォリオに与える影響を和らげ、全体的なリスクを軽減するのに役立ちます。
安全なプラットフォームを選択してください
強力なセキュリティ対策を備えたプラットフォームを選択することは、リスクを最小限に抑える上で重要です。資金の安全性を確保するために、冷蔵庫保管、2要素認証(2FA)、資産保険を提供する取引所を優先させてください。
投資家は、取引所が冷蔵庫(ほとんどの資産をオフラインで保管)、マルチシグネチャウォレット、保険基金(SAFU基金など)、そして強化されたセキュリティのための金融準備を利用しているかどうかを確認すべきです。
例えば、2025年3月9日現在、Gate.ioは100億3280万ドルの財務準備を保有しており、ユーザー資産の保護に強いコミットメントを示しています。
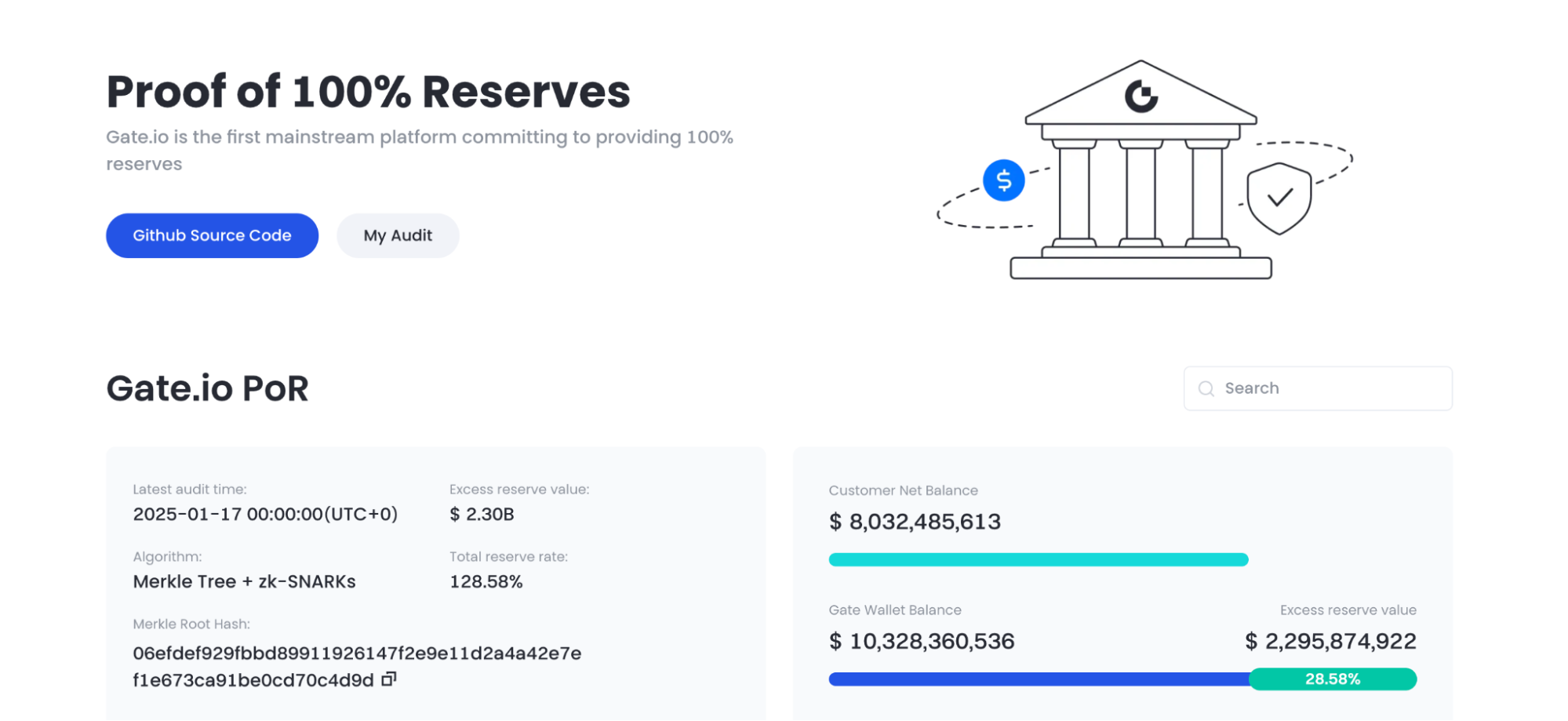
Source: Gate.io
リスク管理ツールの理解と使用
取引所が提供する保険基金と資産追跡技術を活用することは、セキュリティを大幅に向上させることができます。ハッカー攻撃に迅速に対応し、資産回収機能を備えたプラットフォームを選択してください。
さらに、二要素認証(2FA)を有効にし、定期的にアカウントの活動を監視し、怪しい取引を迅速に特定して潜在的な脅威を防止します。

Source: play.google.com/store
長期投資の視点を維持する
短期の市場の変動にもかかわらず、業界のセキュリティ対策やテクノロジーは常に改善されています。過去の攻撃から学び、セキュリティを強化するプロジェクトに投資することで、時間の経過とともにより安定した収益を得ることができます。
フィッシング攻撃とソーシャルエンジニアリングに注意してください
技術の進歩に伴い、ハッカーの攻撃は特にフィッシング詐欺などのソーシャルエンジニアリング手法において、ますます洗練されています。投資家はセキュリティに注意を払い、怪しいリンクをクリックせず、潜在的なセキュリティリスクを防ぐために個人情報を決して共有しないようにする必要があります。
デューディリジェンスを実施し、無謀な投資を避ける
投資する前に、プロジェクトの背景、チーム、セキュリティ対策を徹底的に調査してください。盲目的に市場のトレンドに従うのを避け、堅固な技術基盤と実証されたセキュリティ対策を持つプロジェクトに焦点を当ててください。
業界のトレンドを把握し、情報をキープする
暗号資産業界は急速に進化しており、投資家はセキュリティプロトコル、市場トレンド、技術の進歩の知識を継続的に更新する必要があります。業界の動向についていくことで、投資家は複雑な市場でよりよく情報を得た意思決定をするのに役立ちます。
個人投資家は、セキュリティ意識を高め、プラットフォームを注意深く選択し、多様化とリスク管理ツールを通じてリスクを軽減すべきです。単一障害を避け、長期的視点を採用することにより、投資家はセキュリティの課題を克服し、防衛を継続的に向上させることができるプロジェクトに焦点を当てることができます。
結論
暗号資産業界の急速な発展は、莫大な革新と富の機会をもたらしましたが、セキュリティは依然として最大の課題の1つです。過去数年にわたる主要なハッキング事件は、何十億ドルもの損失をもたらし、また暗号資産取引所、ウォレット、クロスチェーン技術のセキュリティの脆弱性を露呈しました。ハッキング技術がますます洗練され、組織化されたサイバー犯罪集団を巻き込むことが多くなる中、セキュリティ対策の強化と規制フレームワークの強化が業界の成長のための重要な優先事項となっています。
これらの課題にもかかわらず、業界は技術革新や予防機構を通じてセキュリティを向上させるために積極的に取り組んでいます。スマートコントラクトの監査、分散型セキュリティフレームワーク、従業員のセキュリティトレーニングの改善などの対策は、リスクを軽減しユーザーの信頼を高めることを目指しています。
先を見据えると、テクノロジーが進化し規制が改善するにつれて、暗号資産業界はより安全で安定したものになり、広範な採用と社会的受容の道を切り拓くことが期待されています。ただし、セキュリティリスクは長期的な課題として残ります。すべての業界関係者が協力してハッキング攻撃を効果的に防ぎ、マネーロンダリングと戦い、暗号市場の健全な発展を確保することができます。
関連記事

トップ10のビットコインマイニング会社

定量的戦略取引について知っておくべきことすべて

政府効率局(DOGE)のガイド

2024年の日本のWeb3市場:政府の政策、企業のトレンド、そして2025年の展望

Piコインの真実:次のビットコインになる可能性がありますか?




