Qu'est-ce que Super.exchange ? Tout ce que vous devez savoir sur SUPER
Super.exchange est une plateforme d'échange sur chaîne qui combine les lancements de jetons et le trading, fournissant une liquidité stable et une distribution équitable des jetons avec son mécanisme Super Curve.Introduction

Source: Super.exchange
Un catalyseur majeur du supercycle des memecoins de 2024 a été le processus de création et de trading de jetons sans friction et instantané. Des plateformes comme Pump.fun ont simplifié les lancements de jetons, alimentant une croissance explosive des jetons mèmes basés sur Solana. À la mi-2024, Solana avait dépassé Ethereum en tant que blockchain préférée pour les memecoins, grâce à ses frais réduits et à un trading haute vitesse.
Cependant, le mécanisme de lancement de jetons a été critiqué pour son manque d'équité. Les premiers acheteurs, y compris les initiés et les traders de robots, pouvaient exploiter le système en achetant des jetons à des prix plus bas et en les déversant sur les nouveaux entrants plus tard.
La plateforme d'échange Super introduit une approche alternative aux lancements de jetons, avec son mécanisme de courbe de liaison unique offrant une entrée plus équilibrée pour tous les participants. Son jeton natif, $SUPER, incite les traders et est entièrement détenu par la communauté.
Qu'est-ce que Super.exchange?
Super.exchange est une plateforme d'échange décentralisée construite sur la blockchain Solana qui combine un lancement de jetons avec un échange décentralisé. Elle utilise une courbe de liaison infinie, qui ne nécessite pas de fournisseurs de liquidité traditionnels couramment utilisés par les teneurs de marché. Au lieu de cela, elle ajuste automatiquement les prix en fonction de l'offre et de la demande des jetons.
Cette approche aide à créer un pool de liquidité plus stable et empêche l'exploitation précoce des acheteurs, rendant les lancements de jetons plus équitables pour tous les intervenants. La plateforme a son propre jeton, $SUPER, qui est entièrement détenu par la communauté.
Courbes d'allocation dans les cryptomonnaies
Une courbe de liaison est une formule mathématique intégrée dans un contrat intelligent qui détermine dynamiquement le prix d'un jeton en fonction de son offre. En général, plus de jetons sont achetés, plus le prix augmente le long d'une courbe prédéfinie, et lorsque des jetons sont vendus, le prix diminue en conséquence.
Les courbes de liaison créent une liquidité automatisée sur chaîne en garantissant que les jetons peuvent toujours être achetés ou vendus à des prix déterminés de manière algorithmique. Contrairement aux marchés traditionnels, elles fonctionnent indépendamment des carnets de commandes externes, en s'appuyant sur les mécanismes d'offre et de demande au sein du contrat.
Modèle de Pump.fun
Pump.fun utilise un mécanisme de courbe de liaison où de nouveaux jetons sont émis, et leur prix augmente lorsque les utilisateurs achètent. La courbe de liaison se termine une fois que la capitalisation boursière d'un jeton atteint 69 000 $. À ce stade, Pump.fun dépose 12 000 $ de liquidité dans Raydium, une plateforme d'échange décentralisée sur Solana.
Cependant, cette transition vers Raydium introduit une pression de vente et une volatilité des prix, car les premiers acheteurs et traders cherchent à encaisser.
Le modèle CPMM
Le Market Maker à Produit Constant est le modèle populaire adopté par la plupart des plateformes d'échange décentralisées telles que Raydium et Uniswap. Le modèle est basé sur l'équation ; x * y = k
Où;
- x = Quantité de Token A (par exemple, SOL) dans le pool de liquidité.
- y = Quantité de Token B (par exemple, un jeton mème).
- k = Produit constant, ce qui signifie que la liquidité totale reste inchangée.
Par conséquent, en trading; Lorsqu'un utilisateur achète Token B, il ajoute plus de Token A (SOL) dans le pool, ce qui réduit l'offre disponible de Token B, puisque xy doit rester constant, le prix du Token B augmente. De plus, lorsque qu'un utilisateur vend du Token B, il ajoute plus de Token B dans le pool, ce qui réduit l'offre disponible de Token A (SOL), et comme xy doit rester constant, le prix du Token B diminue.
Lorsque l'offre d'un jeton diminue, son prix augmente en raison de la règle du produit constant. La formule empêche l'épuisement complet de la liquidité mais peut entraîner un fort glissement pour les grosses transactions.
Comment fonctionne Super.Exchange ?

Le mécanisme de lancement de jetons sur Super.exchange est basé sur la Super Curve, une courbe composite qui regroupe sept courbes d'adhésion définies par :
∀ . y = k
Où 𝑥 est l'offre de jetons, et 𝑦 est le prix, et n est fixé à 32, 16, 8, 4, 3, 2 et 1.
Cela signifie que lorsque 𝑥 (offre de jetons ou liquidité) change, 𝑦 (prix) s'ajuste selon une courbe exponentielle définie par la valeur de 𝑛 qui est prédéfinie dans les sept courbes de liaison de la Super Curve.
La conception de la Super Curve empêche les premiers acheteurs d'accumuler de manière injuste de grandes quantités de jetons à bas prix. Par exemple, l'acquisition de 80% de l'offre d'un jeton sur Super.exchange entraîne une augmentation de prix de 40 269 fois, contre seulement 15 fois sur des plateformes traditionnelles de courbe de liaison comme Pump.fun.

Comparaison de la croissance d'un jeton utilisant Super Curve par rapport aux courbes de liaison traditionnelles

Caractéristiques de profondeur du marché de la Super Courbe par rapport aux modèles traditionnels
Effet de différentes valeurs de n
Au début d'un lancement de jeton, n est fixé à un niveau élevé et diminue avec le temps
- n = 32 → Le prix augmente très rapidement avec de petits achats, et les premiers acheteurs paient significativement plus pour chaque jeton supplémentaire, empêchant une accumulation précoce extrême.
- Si n = 8 ou 4 → la croissance des prix ralentit mais reste positive, mais les premiers acheteurs n'obtiennent plus une remise extrême par rapport aux nouveaux acheteurs.
- Si n = 1 → L'appréciation des prix est progressive et durable, et la courbe d'obligations se comporte plus près de la formule traditionnelle (x * y = k).
Le modèle Super.exchange vs le modèle Pump.fun
Le tableau ici compare les fonctionnalités du modèle Super.plateforme d'échange avec Pump.fun

Navigation sur Super.plateforme d'échange
Création d'un nouveau jeton
Pour créer un nouveau jeton sur la plateforme d'échange Super, vous devez fournir une image, un ticker et un nom. Il est recommandé de remplir les champs optionnels, y compris les liens vers Twitter, Telegram et le site web du projet. La création de jeton est gratuite.
Pour éviter toute confusion et tout risque d'escroquerie lié aux jetons avec des identifiants en double, Super.exchange attribue des identifiants uniques à chaque jeton. Une fois créés, toutes les modifications de ses détails ne peuvent être apportées que par le biais d'un processus de vote sur proposition.

Source: Super.exchange

Trading sur Super.exchange
Avant d'interagir avec la plateforme d'échange Super.exchange, vous devrezachatSolana (SOL) de Gate.com et le retirer à votre adresse de portefeuille connectée à Super.exchange.
Pour acheter un jeton sur Super.exchange;
- À partir de la page d'accueil, connectez votre portefeuille,
- Définir le montant d'achat rapide en SOL.
- Cliquez sur le bouton Acheter à côté de votre jeton préféré
- Confirmez la transaction dans votre portefeuille.

Source :Super.plateforme d'échange
Sinon, vous pouvez acheter et vendre depuis la page Détails du jeton,
- Confirmez le ticker pour vous assurer que c'est bien la pièce exacte que vous souhaitez échanger.
- Sélectionnez si vous souhaitez acheter ou vendre.
- Entrez le montant de la transaction.
- Pour les achats, vous pouvez saisir le montant en SOL ou en jeton.
- Pour vendre, le montant est saisi en pièces par défaut.
- Vérifiez la limite de glissement et les frais de priorité; ajustez si nécessaire.
- Cliquez sur "Passer un ordre" et approuvez la transaction dans votre portefeuille.
- Une fois que la transaction est confirmée sur la chaîne, les détails de l'échange apparaîtront dans la section en bas à gauche de la page. Cela peut prendre quelques secondes pour se rafraîchir.
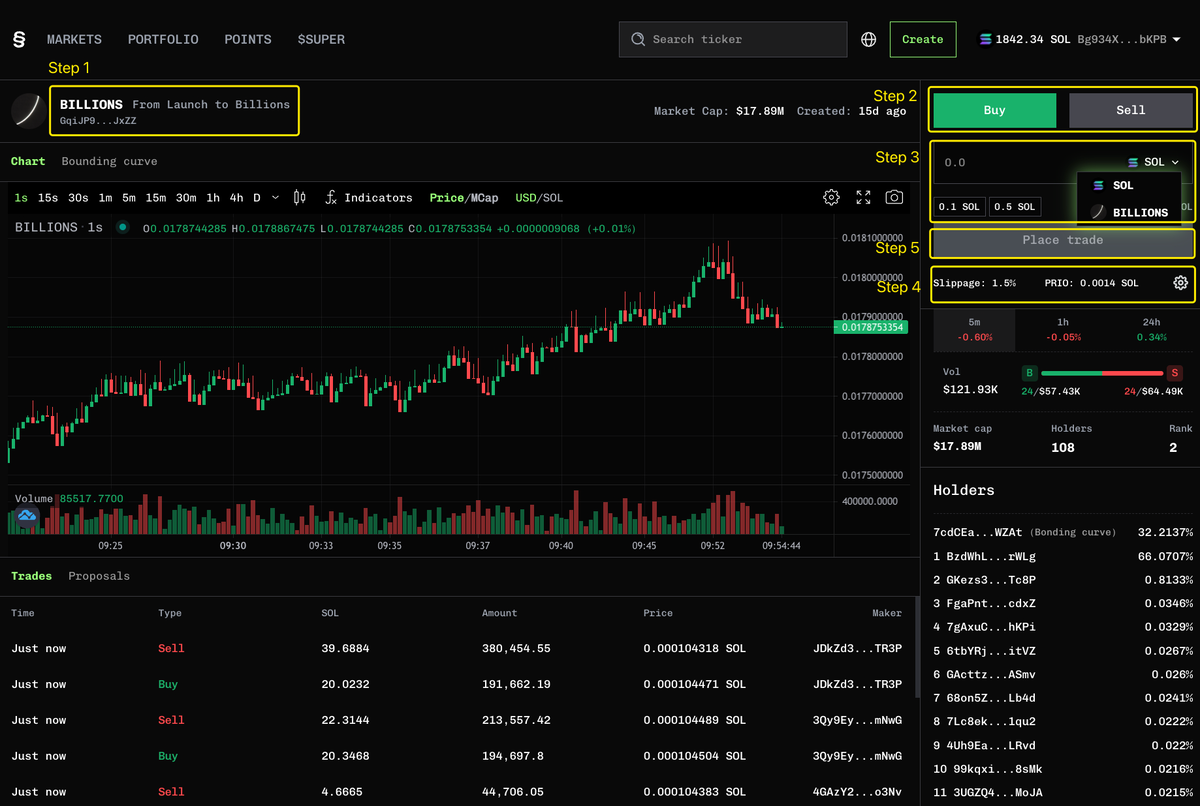
Source: Super.exchange
Configurer les paramètres de trading
Sur Super.exchange, vous pouvez personnaliser deux paramètres : limite de glissement et frais de priorité.
Limite de glissement
Le glissement est la différence entre le prix attendu d'un échange et le prix final d'exécution, souvent causé par la volatilité du marché. Les utilisateurs peuvent définir leur limite de glissement et si le prix évolue au-delà du pourcentage spécifié pendant l'exécution, la transaction est automatiquement annulée. La limite de glissement recommandée est de 0,1% à 2%.
Frais prioritaire
Sur la blockchain Solana, chaque transaction entraîne des frais de base de 0,000005 SOL. À mesure que le trafic réseau augmente, les transactions concourent pour un espace limité. Les utilisateurs peuvent payer des frais de priorité pour une exécution plus rapide.
Frais de transaction
Super Exchange met en œuvre un modèle de frais de trading échelonnés basé sur la capitalisation boursière (MC) d’un token :

Qu'est-ce que le jeton SUPER ?

SUPER est le jeton natif de Super.exchange, gagné en accumulant des points à travers des échanges ou en invitant de nouveaux utilisateurs, et peut être échangé contre des jetons SUPER sur une base de 1:1.
Les points sont distribués à travers des cycles de 5 minutes, et le montant distribué par cycle devrait diminuer à mesure que la capitalisation boursière de SUPER augmente.
La distribution est basée sur la formule;
Plafond des points d'intervalle = SUPER restant dans la courbe de cotation / 28800
Les points disponibles à tout moment seront répartis à 80/20. 80% pour les traders et 20% pour les références.
Distribution de jetons
SUPER a un total de 1 milliard de jetons et est à 100% la propriété de la communauté sans allocation d'investisseurs ou d'équipe.
50 % des frais de négociation seront utilisés pour les rachats et les brûlures de SUPER, ce qui réduira l’offre au fil du temps.

Source: SUPER.exchange
Est-ce que Super.exchange est un bon investissement?
Super.exchange construit une plateforme qui protège les traders des schémas habituels de pump-and-dump en introduisant la Courbe Super. Ce mécanisme de courbe d'obligation empêche les premiers acheteurs d'accumuler de grandes parties de l'offre d'un jeton à des prix disproportionnellement bas.
Le jeton $SUPER lui-même fonctionne principalement comme un mécanisme de récompense. Les utilisateurs gagnent des points grâce à l’échange et au parrainage, qui peuvent être échangés contre l’achat de jetons $SUPER.
Cependant, sa viabilité à long terme dépend de l'adoption par les utilisateurs, de l'activité commerciale soutenue, et de sa capacité à établir une utilité plus profonde pour son jeton natif au-delà des rachats et des brûlures.
Investir sur Super.exchange comporte des risques tels que la volatilité du marché et les changements réglementaires. Les investisseurs doivent mener des recherches approfondies et évaluer leur tolérance au risque, car les investissements en crypto ne garantissent pas de profits et peuvent entraîner des pertes en capital.
Articles Connexes

Comment miser sur l'ETH?

Top 10 Plateformes de trading de jetons MEME

Qu'est-ce que le Dogecoin ?

Qu'est ce que Solana?

Qu'est-ce que Coti ? Tout ce qu'il faut savoir sur l'ICOT


